DHCP Explained: The Internet’s Automatic Address Book
Why Your Devices Connect Instantly (Without You Typing Anything)
Ever wondered how your phone, laptop, and smart TV all get online the moment you join a Wi-Fi network? The magic behind this convenience is called DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)—the internet’s version of an automatic address assigner.
Here’s how it works in plain English, why it matters, and what happens when it fails.
🌐 What Is DHCP?
Imagine a hotel receptionist who:
Checks you in (gives you a room number).
Tells you the breakfast timings (network rules).
Recycles your room when you leave (for new guests).
That’s essentially what DHCP does for devices on a network:
✔ Assigns IP addresses (like room numbers).
✔ Provides network settings (subnet mask, gateway, DNS).
✔ Manages addresses efficiently (no overlaps).
🔧 How DHCP Works in 4 Simple Steps
1. Device: “I Need an Address!” (DHCP Discover)
When you connect to Wi-Fi, your device shouts: “Hey, is there a DHCP server here?”
This is a broadcast message (sent to everyone on the network).
2. Server: “Here’s Your Key” (DHCP Offer)
The router (DHCP server) responds: “Use IP 192.168.1.10 for 24 hours.”
Includes extra info:
Subnet mask (defines network size).
Default gateway (the “exit door” to the internet).
DNS server (translates google.com → IP).
3. Device: “I’ll Take It!” (DHCP Request)
Your device confirms: “Thanks, I’ll use 192.168.1.10.”
4. Server: “Approved!” (DHCP Acknowledgment)
The server finalizes the lease and logs it.
Total time: Less than a second!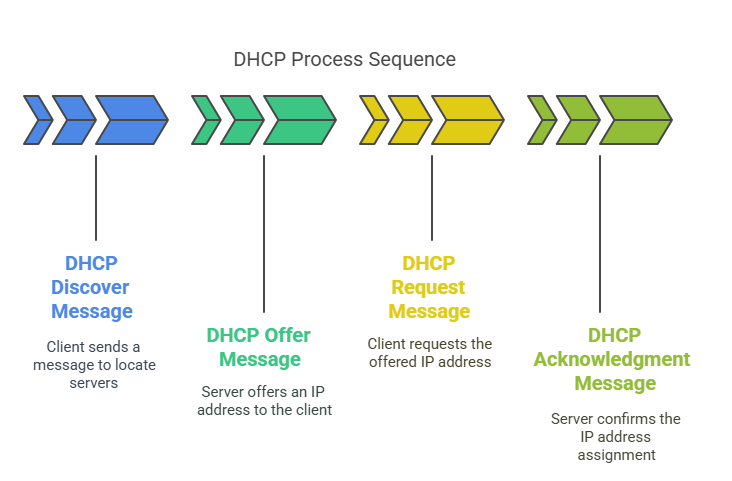
🏠 Real-World DHCP Examples
Home Networks:
Your router acts as the DHCP server.
Assigns IPs to phones, laptops, smart TVs.
Office Networks:
Dedicated servers handle 1000+ devices.
Uses reservations for printers/servers (always same IP).
Coffee Shop Wi-Fi:
DHCP leases last 1-4 hours (for rotating guests)
⚠️ What Happens When DHCP Fails?
“No internet” errors (even with strong Wi-Fi).
IP conflicts (two devices with the same address).
Slow connections (devices use fallback self-assigned IPs).
Fix It With:
Restart your router (resets DHCP).
Check for IP conflicts (ping tests).
Enable DHCP (if accidentally turned off).
DHCP vs. Static IP: Which is Better?
| Feature | DHCP | Static IP |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Automatic | Manual |
| Best for | Phones, laptops | Servers, printers |
| Maintenance | Zero effort | Manual tracking |
| Flexibility | Great for changing networks | Never changes |
Rule of Thumb:
Use DHCP for devices that move (phones, tablets).
Use static IPs for critical gear (security cameras, NAS).
🔍 Fun Fact:
Your IP lease has an expiry time (usually 24 hours). Ever noticed your phone’s IP change? That’s DHCP renewing the lease!
💡 Why This Matters to You
No manual IP setups (plug and play).
Prevents address chaos (no two devices clash).
The reason you can join any Wi-Fi instantly.
Next time your laptop connects seamlessly, thank DHCP—the silent hero of networking!